In this article, we will show you how to change the date and time format in WordPress. If you want to abbreviate the month, hide the year, or display the time, you can use the built-in functions in WordPress to customize the format.
To modify your date and time format, go to the Settings » General page in the WordPress admin area and scroll down to the timezone section.
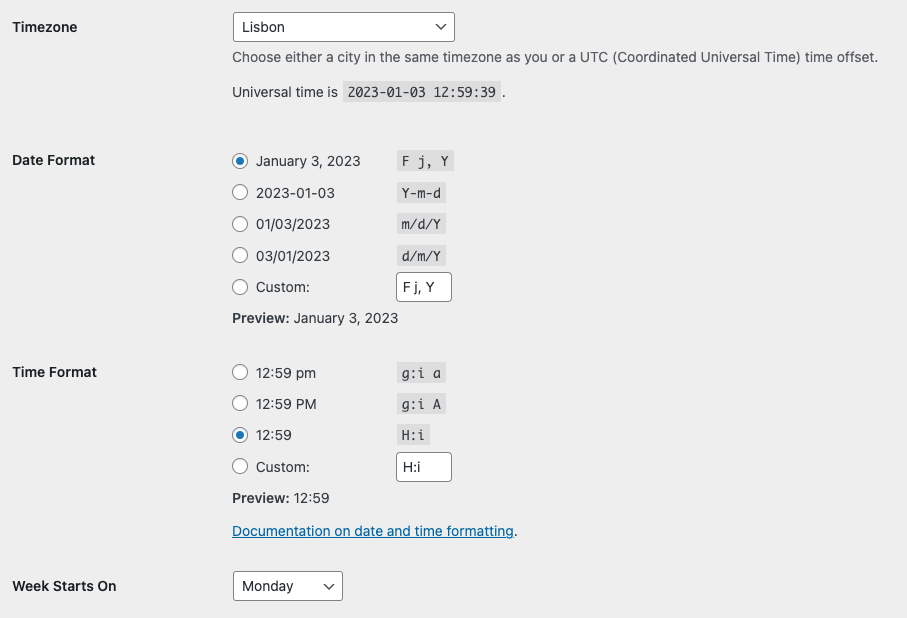
You can select a timezone for your website and choose a date and time format. There are several built-in options available, or you can create a custom format by entering it manually. Simply click on the radio button next to your preferred option.
If you want to change the date and time format on your WordPress website using the template file, you can locate the WordPress tag functions the_date() and the_time(). These functions will display the date and time format that is set in your WordPress dashboard. This option is useful if your theme or plugin files have their own default date and time format.
Time and Date Formats in WordPress
On the Settings » General page, you can find a series of characters called the format string next to each option in the Date Format and Time Format sections. These format characters represent different elements of the date and time structure, and can be used to create a custom string that displays the date and time in a specific format.
For example, in the m/d/Y format string, the characters represent the following:
- m: the numeric month with a leading zero
- d: the numeric day of the month with a leading zero
- Y: the four-digit year
So this string would output the date as 11/18/2022.
Since WordPress is developed in PHP, you can use the following date and time format characters to create your own custom structure string or take it directly from the PHP website.
| Format Character | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Day of the Month | ||
| d | Numeric, with leading zeros | 01-31 |
| j | Numeric, without leading zeros | 1-31 |
| S | English suffix for the day of the month | st, nd, th in the 1st, 2nd, or 15th |
| Format Character | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Weekday | | |
| I | Full name (lowercase ‘L’) | Sunday – Saturday |
| j | Numeric, without leading zeros | 1-31 |
| D | Three letter name | Mon – Sun |
| Format Character | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Month | | |
| m | Numeric, with leading zeros | 01-12 |
| n | Numeric, without leading zeros | 1-12 |
| F | Textual full | January – December |
| M | Textual three letters | Jan – Dec |
| Format Character | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Year | | |
| Y | Numeric, 4 digits | Eg., 2018, 2023 |
| y | Numeric, 2 digits | Eg., 18, 23 |
| Format Character | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Time | | |
| a | Lowercase | am, pm |
| A | Uppercase | AM, PM |
| g | Hour, 12-hour, without leading zeros | 1-12 |
| h | Hour, 12-hour, with leading zeros | 01-12 |
| G | Hour, 24-hour, without leading zeros | 0-23 |
| H | Hour, 24-hour, with leading zeros | 00-23 |
| i | Minutes, with leading zeros | 00-59 |
| s | Seconds, with leading zeros | 00-59 |
| T | Timezone abbreviation | Eg., EST, MDT … |
| Format Character | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Full Date/Time | | |
| c | ISO 8601 | 2004-02-12T15:19:21+00:00 |
| r | RFC 2822 | Thu, 21 Dec 2000 16:01:07 +0200 |
| U | Unix timestamp (seconds since Unix Epoch) | 1455880176 |
Here are some examples of date format with the resulting output.
| Format String | Example |
|---|---|
| F j, Y g:i a | November 6, 2010 12:50 am |
| F j, Y | November 6, 2010 |
| F, Y | November, 2010 |
| g:i a | 12:50 am |
| g:i:s a | 12:50:48 am |
| l, F jS, Y | Saturday, November 6th, 2010 |
| M j, Y @ G:i | Nov 6, 2010 @ 0:50 |
| Y/m/d at g:i A | 2010/11/06 at 12:50 AM |
| Y/m/d at g:ia | 2010/11/06 at 12:50am |
| Y/m/d g:i:s A | 2010/11/06 12:50:48 AM |
| Y/m/d | 2010/11/06 |
Additional Customization Options
Localizing
To localize the date and time on your WordPress site, you can use the wp_date() function. This function works similarly to the PHP date() function, but it also translates things like month names and weekdays into the current locale for the site. You can use wp_date() instead of date(), using the same arguments.
For example, instead of using date('F jS, Y'), you can use wp_date('F jS, Y'). This will translate the month and day names into the current locale for the site.
Escaping
It’s important to note that some letters do not have an associated format in the PHP date() function. For example, if you pass the letter ‘x’ in the format string, it will currently return a literal ‘x’. However, this could change in the future and ‘x’ may have a format associated with it.
To prevent this from causing issues, it’s recommended to always escape literal characters in a date-formatted string using a backlash “\”. For example, in the following example, every letter in the word ‘of’ is escaped:
wp_date( __( 'l jS \o\f F Y', 'textdomain' ) );This example will render as follows on the front end of your site: Monday 24th of October 2022.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the WordPress date() function allows you to format and display the date and time on your website according to your preferred structure. You can use a variety of predefined format characters, or create a custom format string using a combination of these characters.
To localize the date and time to the current locale for your site, you can use the wp_date() function instead of date(). It’s important to remember to escape literal characters in your format string using a backslash “\”, as this will ensure that your format is displayed correctly even if the meaning of certain characters changes in the future.
By using these functions, you can easily customize the way the date and time are displayed on your WordPress website.


